THE UPSIDE CAP IN ALL BUFFER SERIES OFFERINGS (regardless of the level of downside protection) is mostly influenced by two factors: interest rates and market volatility. Obviously, investors considering an allocation in Buffer ETFs want the highest upside cap possible during the outcome period. A high upside cap allows investors to participate in gains to the fullest extent possible. However, there are times when upside caps can be relatively low and other times when they are well above the historical average annual return of the stock market. Let’s look at how interest rates and market volatility influence the upside caps on Buffer ETFs.
- Interest Rates
An increase in interest rates will drive up call premiums and cause put premiums to decrease. Call options are positively influenced by an increase in interest rates, and puts are negatively influenced.
To understand why, you need to think about the effect of interest rates when comparing an option position to simply owning a stock or stock index. Since it is much cheaper to buy a call option than 100 shares of a stock, a call buyer is willing to pay more for an option when interest rates are relatively high. The reason is the investor can invest the difference in the capital required between the two positions.
Let’s look at some comparative examples (Source: Shobhit Seth, Investopedia) that make it easier to understand why interest rates positively influence call options and negatively impact put options.
Rising interest rates positively impact call options
Purchasing 100 shares of a stock trading at $100 will require $10,000, which, assuming a trader borrows money for trading, will lead to interest payments on the borrowed capital. Purchasing the call option at $12 in a lot of 100 contracts will cost only $1,200, yet the profit potential will remain the same as that of the long stock position.
Effectively, the differential of $8,800 will result in savings of outgoing interest payments on this loaned amount. In addition, the saved capital of $8,800 can be kept in an interest-bearing account and will result in interest income. A 5% risk-free interest rate will generate $440 in one year.
Therefore, an increase in interest rates will lead to saving in outgoing interest on the loaned amount and an increase in the amount of interest income on the savings account. Both will be positive for call option pricing. Effectively, a call option’s price increases to reflect this benefit from increased interest rates.
Rising interest rates negatively impact put options
Theoretically, shorting a stock with the objective of benefitting from a price decline, will bring in cash to the short seller. Buying a put has a similar benefit from price declines, but comes at a cost as the put option premium must be paid. This case has two different scenarios: cash received by shorting a stock can earn interest for the trader, while cash spent in buying puts is interest payable (assuming the trader is borrowing money to buy puts).
With an increase in interest rates, shorting stock becomes more profitable than buying puts, as the former generates income and the latter does the opposite. Thus, put option prices are impacted negatively by rising interest rates. - Volatility
When markets are volatile, it simply means returns are going to be volatile too, in either direction, up or down. It also means the level of uncertainty is high and this positively impacts the value of both call and put options. Call and put options actually gain in value when volatility increases. Only market volatility impacts call and put options in the same direction.
When markets are in a downtrend, volatility generally increases. Conversely, market uptrends usually cause volatility to fall. Higher volatility indicates that greater option price movement is expected in the future.
Higher volatility means greater upside risk, but higher downside risk too. This rule applies to both call and put options. This is why higher volatility makes both call and put options more valuable.
As volatility increases, the prices of all options – both calls and puts and at all strike prices – tend to rise. The greater volatility increases the chances of all options finishing “in-the-money” therefore making all options more valuable.
Option pricing is a complex process. Multiple factors impact option valuations, which can lead to very high variations in option prices over the short term. Call and put option premiums are impacted inversely as interest rates change. However, volatility will positively impact both call and put prices.
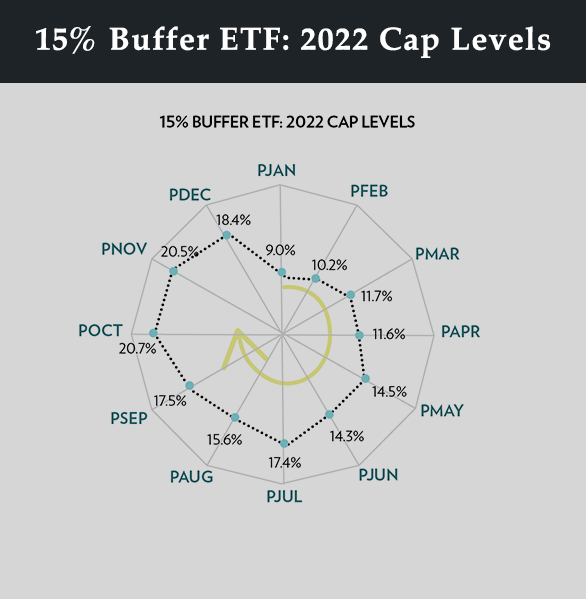
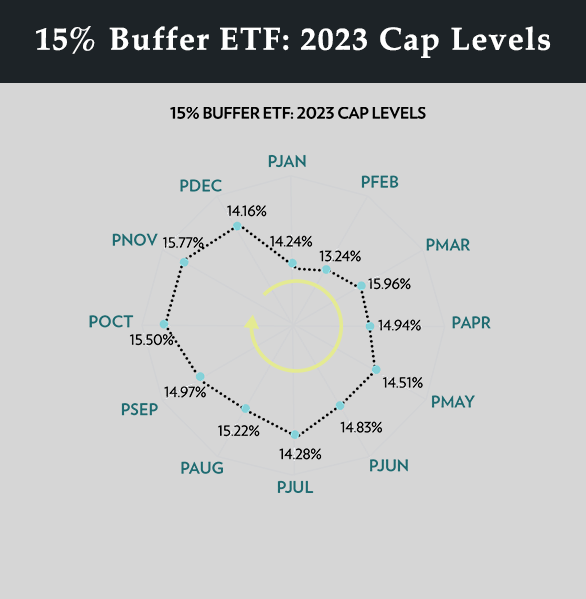
Innovator’s U.S. Equity Power Buffer Series Cap Levels (before fees): 2022 and 2023
Innovator’s U.S. Equity Power Buffer series cap levels (before fees) are shown for 2022 and 2023. The Power Buffers offered 15% downside protection at the start of each reset date, with variable upside caps throughout 2022-2023.
The upside caps greatly increased throughout 2022 as the bear market worsened and volatility increased as stock prices dropped. The upside caps peaked in October and November. By comparing the lowest cap level of 9% in January, to the highest cap level of 20.7% in October, you can see how much volatility affected option prices on the reference asset (SPY). That’s more than a 100% increase in the cap level in less than a year! Again, periods of high volatility will typically push cap levels higher.
In 2023, the upside caps remained fairly consistent (mid-teens). Volatility had subsided from elevated 2022 readings, but higher interest rates helped keep the caps attractive (13.24% – 15.96%), and well above the historical average annual returns of the stock market (10%).
The relatively high upside caps available during both 2022 and 2023 provided an attractive risk vs. reward opportunity for investors looking for a defined level of downside protection, but also with compelling upside profit potential.